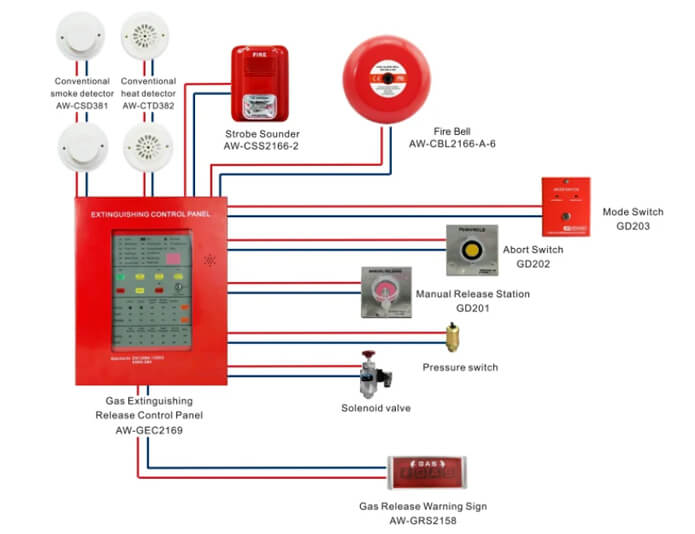
A fire alarm system is a network of devices designed to detect the outbreak of fire by monitoring environmental changes associated with combustion. These changes can include smoke, heat, flame, and a rise in carbon monoxide levels. Once a fire is detected, the system activates an alarm to notify people in the area, allowing them to evacuate safely. Additionally, the system can be configured to automatically activate firefighting equipment, such as aerosol fire extinguishers, to suppress the fire.
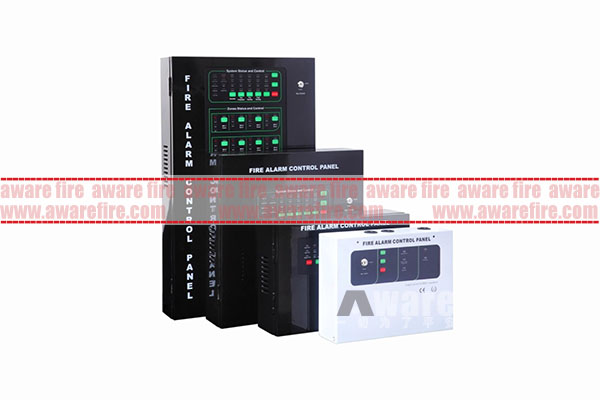
A typical fire alarm system consists of several components, including sensors (or detectors), a control panel, and notification appliances. The sensors are strategically placed throughout the building to detect changes in the environment that indicate the presence of fire. The control panel receives signals from the sensors, processes them, and determines whether to activate the alarm. If the alarm is activated, the notification appliances (such as horns, strobe lights, or both) sound and flash to alert people to evacuate.
Modern fire alarm systems often include additional features for enhanced safety and efficiency. These can include integrated smoke control systems to manage smoke movement in the building, voice evacuation systems to provide instructions to occupants during an emergency, and interfaces with other building systems, such as HVAC, to facilitate evacuation and firefighting efforts.
Regular inspection, testing, and maintenance of a fire alarm system are crucial to ensure its reliability and effectiveness. This includes checking the sensors for proper operation, testing the alarm notification system, and verifying that the control panel and other components are in good working order.
Overall, a fire alarm system is a crucial element of a comprehensive fire safety plan, providing early warning and notification to help mitigate the potential damage and risk to life caused by fire.
Remark: the fire alarm system almost can work with all types of fire suppression systems.